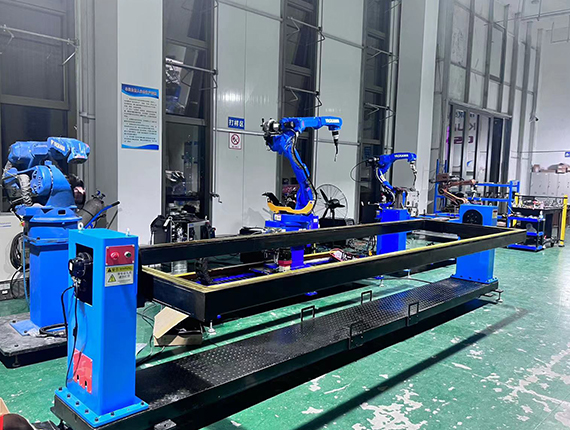
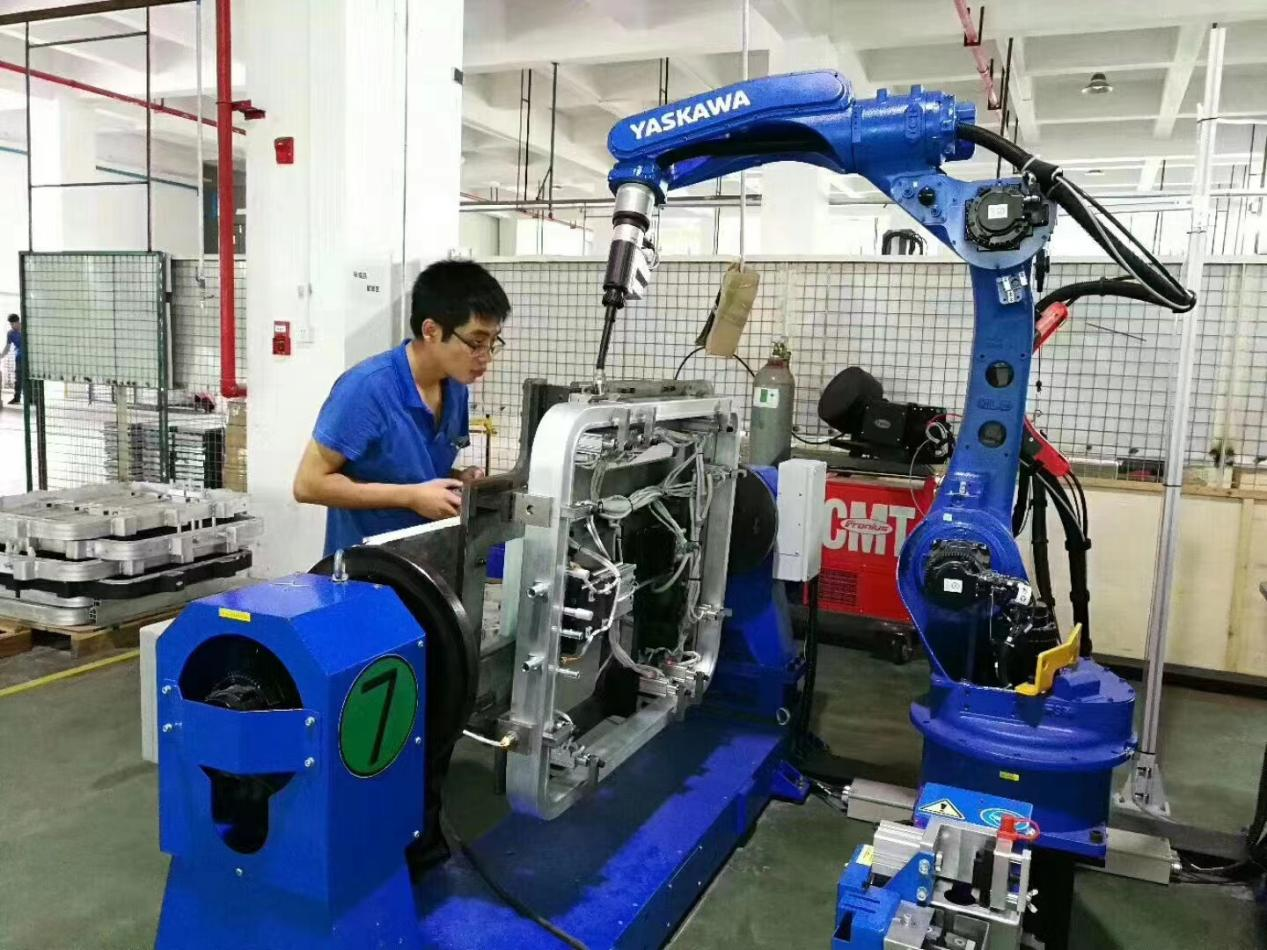
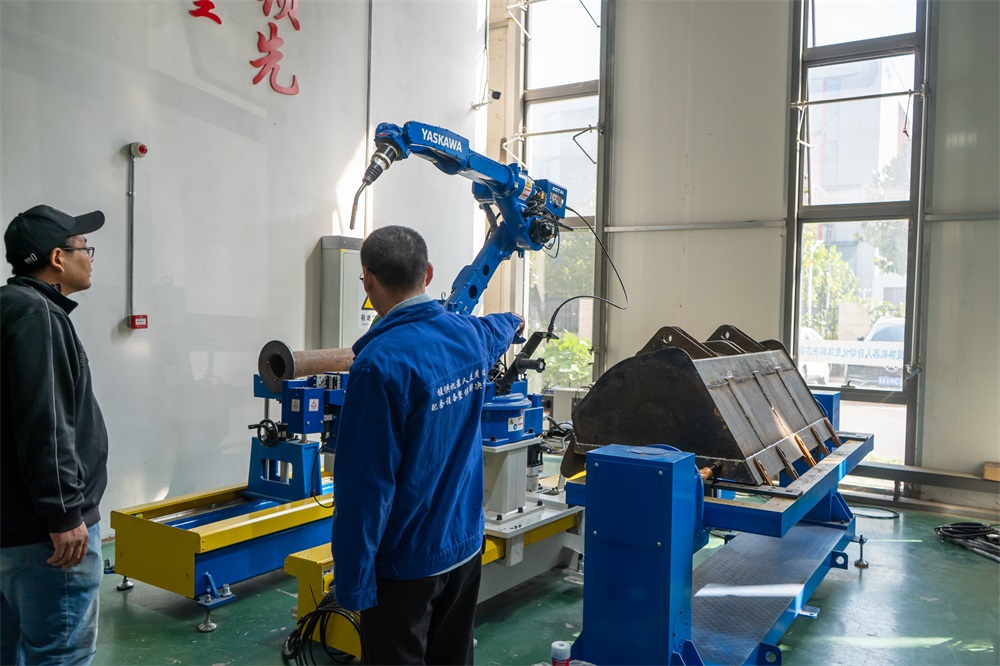
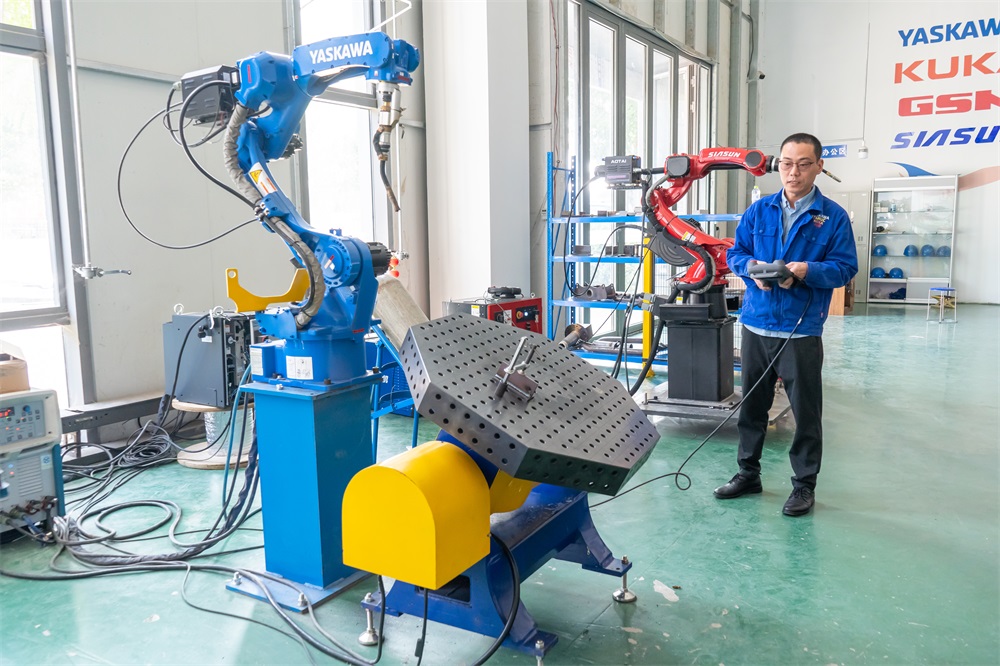
1.能夠根據(jù)特殊的焊接模式來(lái)調(diào)整自動(dòng)化的焊接,穩(wěn)定和提高焊接質(zhì)量,能將焊接質(zhì)量以數(shù)值的形式反映出來(lái);
1. Able to adjust automated welding according to special welding modes, stabilize and improve welding quality, and reflect welding quality in numerical form;
2.提高勞動(dòng)生產(chǎn)率;
2. Improve labor productivity;
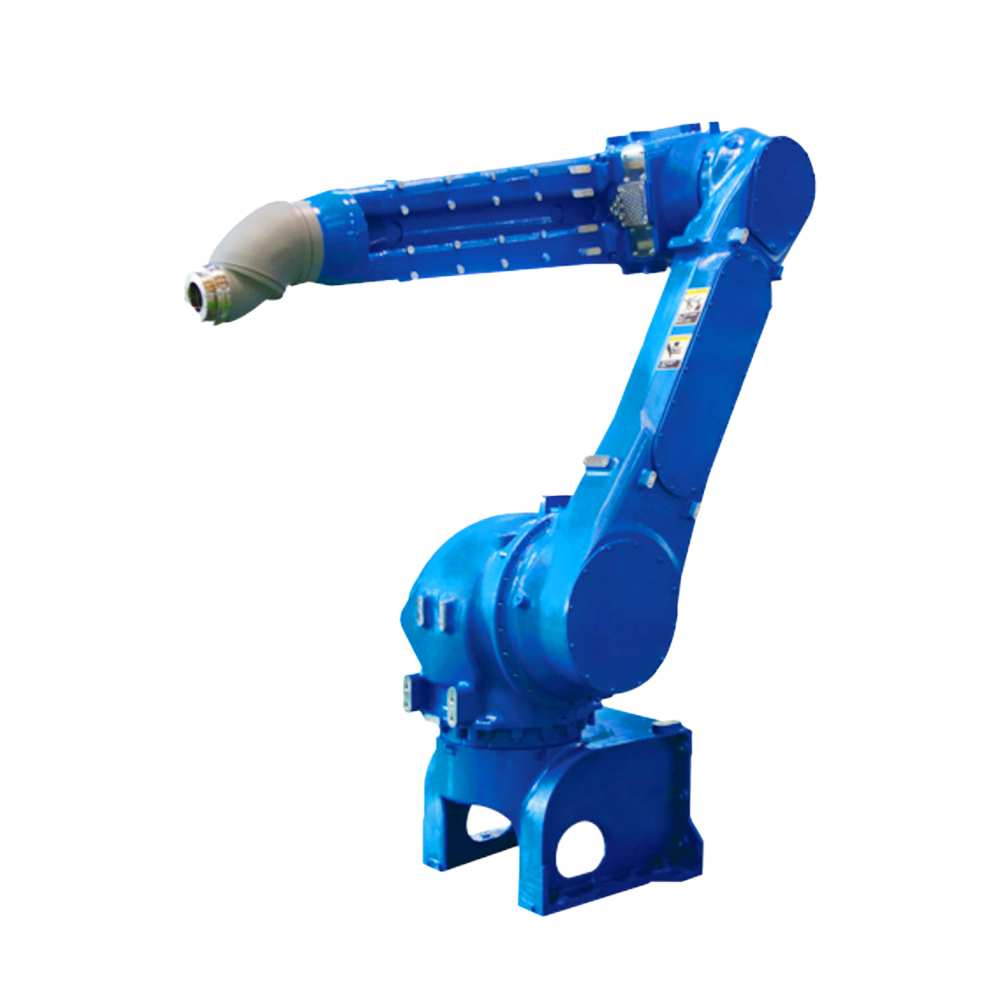

3.改善工人勞動(dòng)強(qiáng)度,可在有害環(huán)境下工作;
3. Improve the labor intensity of workers and enable them to work in hazardous environments;
4.降低了對(duì)工人操作技術(shù)的要求;
4. Reduced the requirements for workers' operational skills;
5.縮短了產(chǎn)品改型換代的準(zhǔn)備周期,減少相應(yīng)的設(shè)備投資。
5. Shortened the preparation cycle for product upgrades and reduced corresponding equipment investment.
6.對(duì)前道工序的加工精度要求高,一般應(yīng)控制在0.5毫米左右
6. high precision requirements for the previous process, generally controlled at around 0.5 millimeters
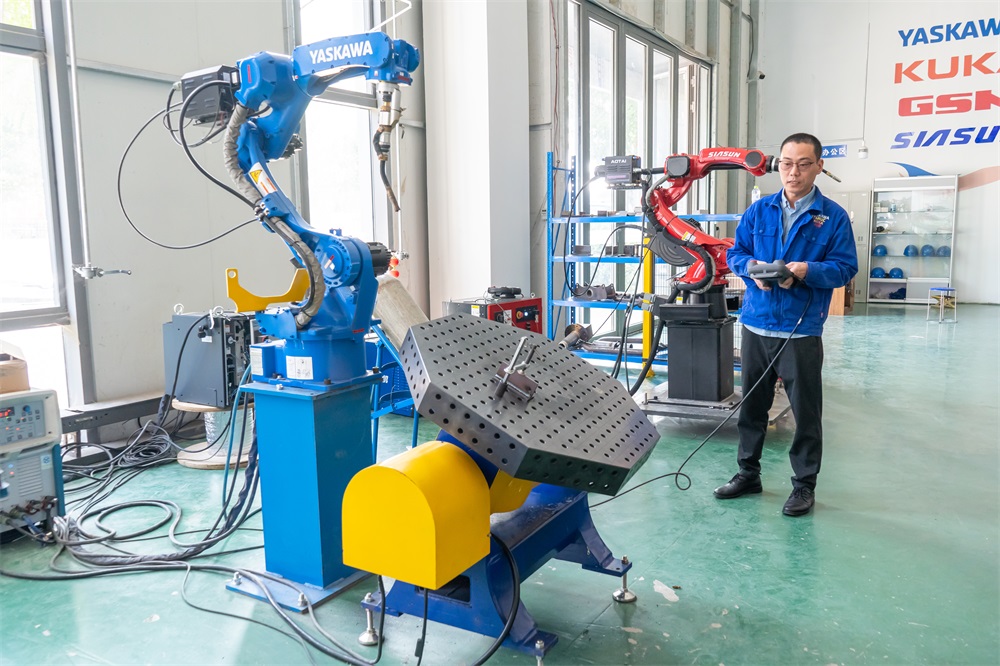
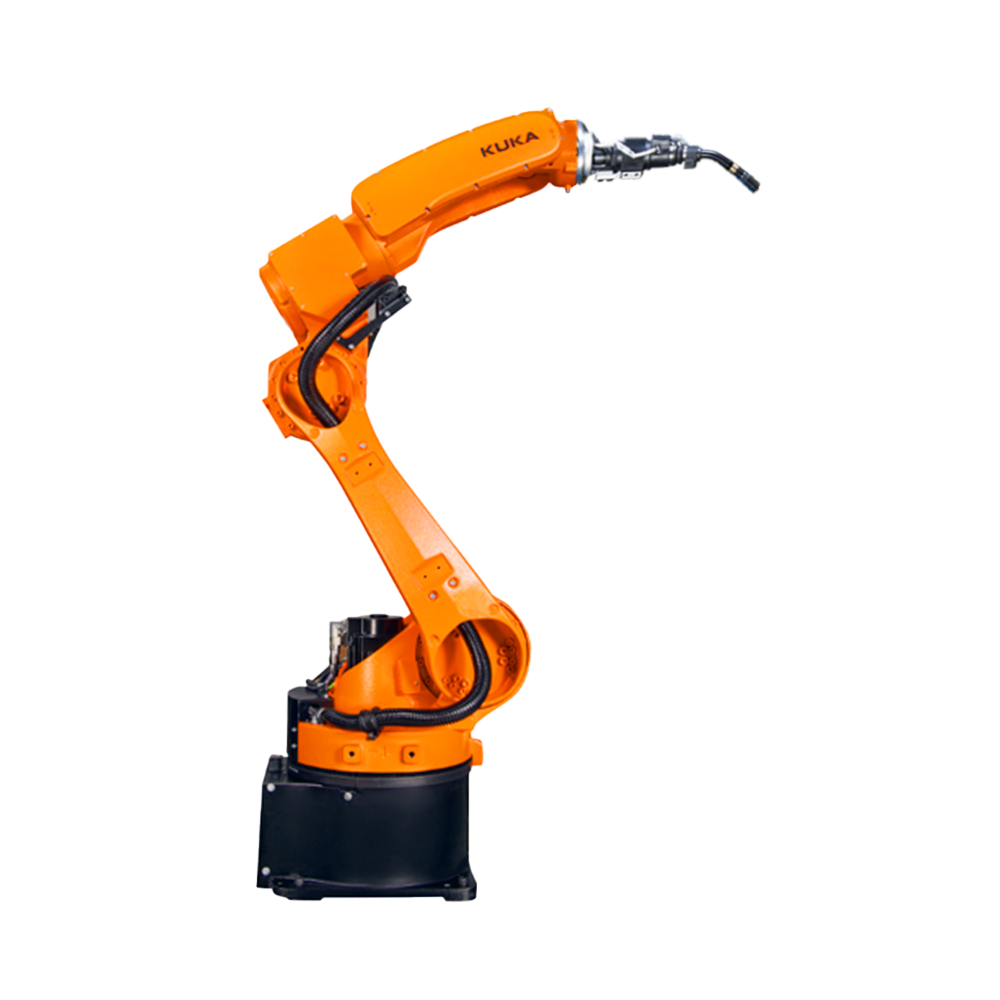
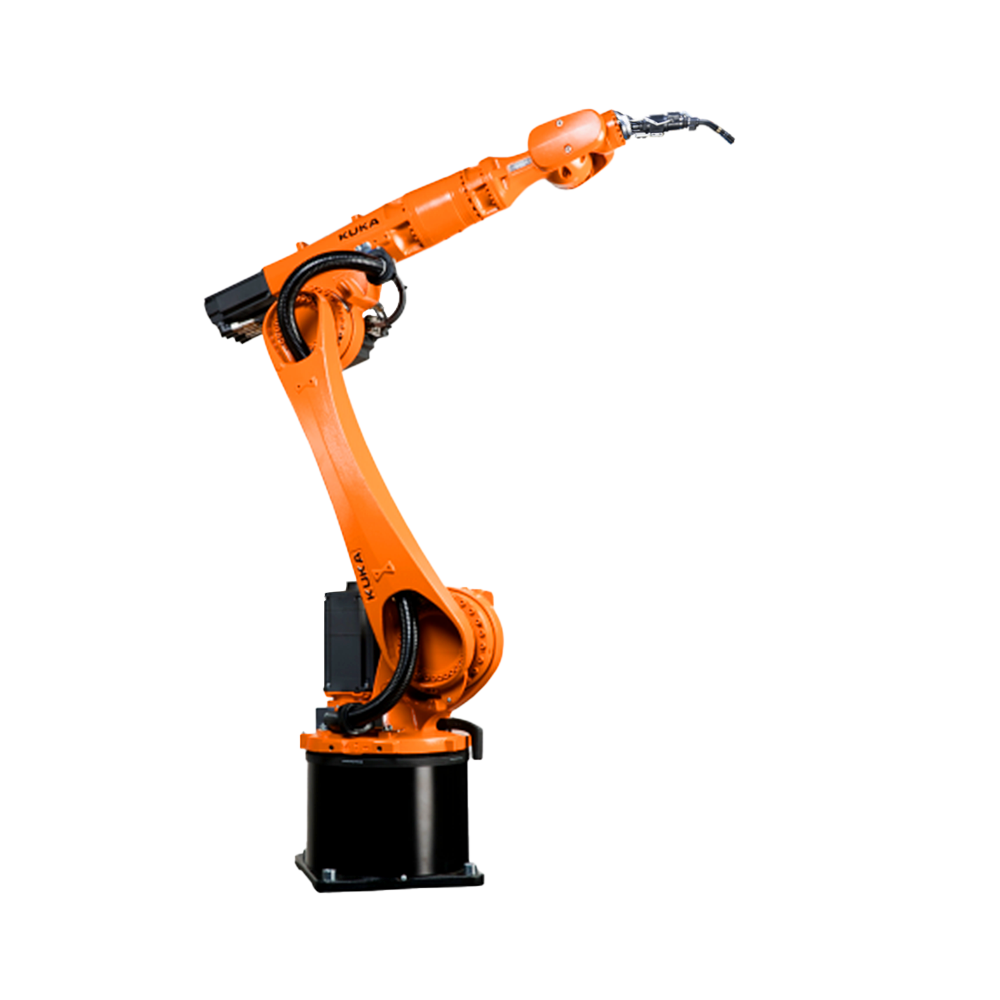
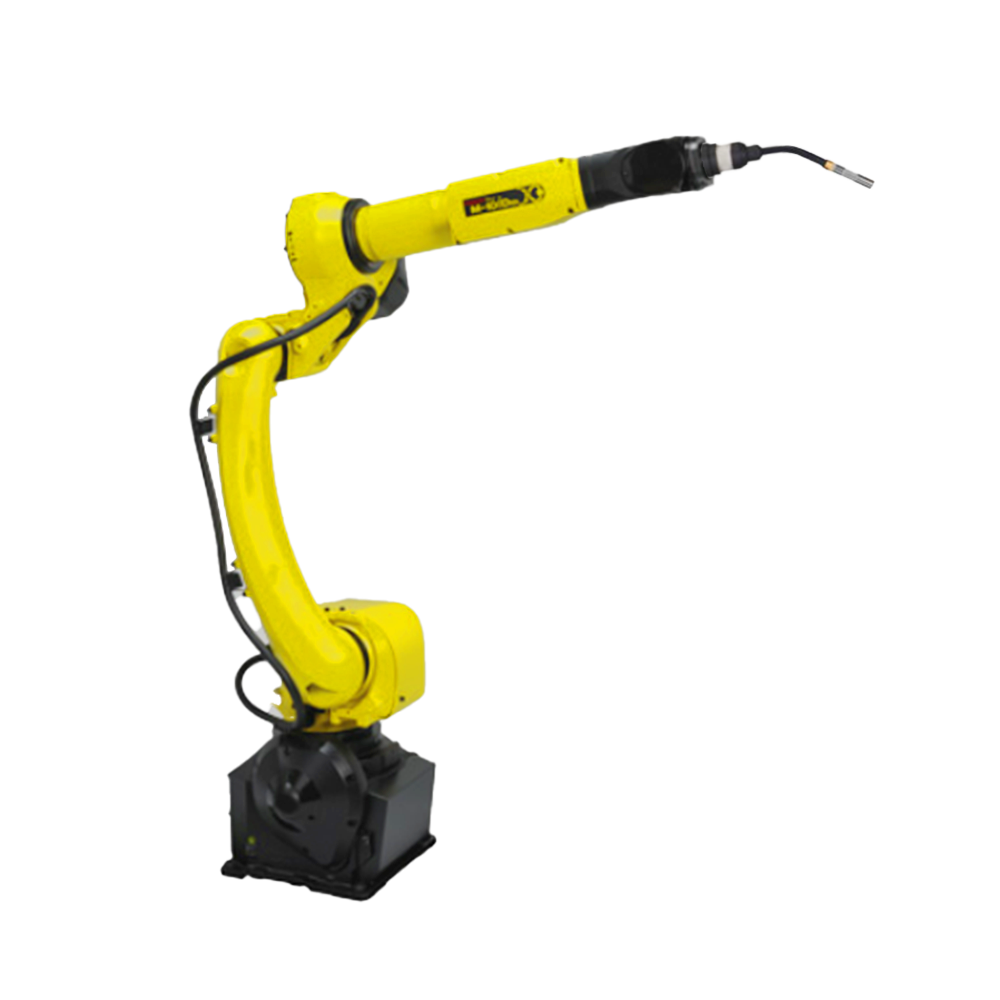
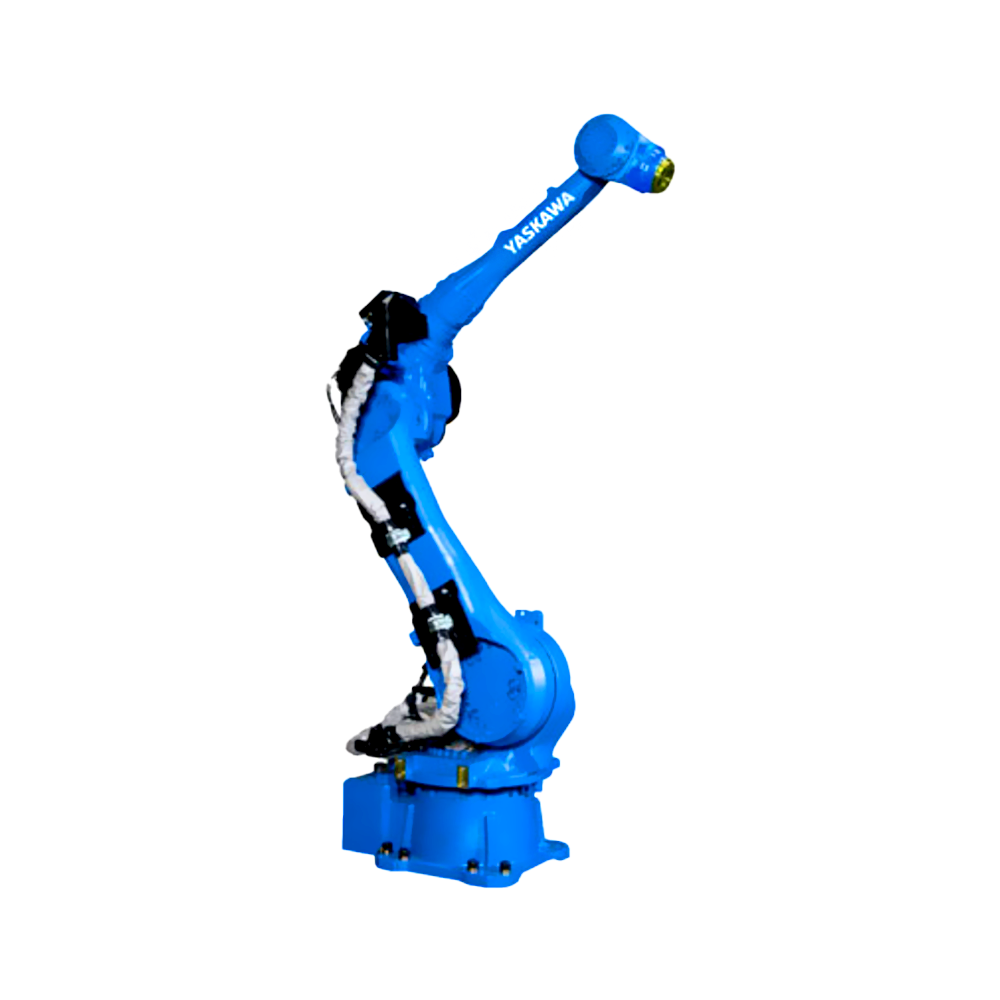
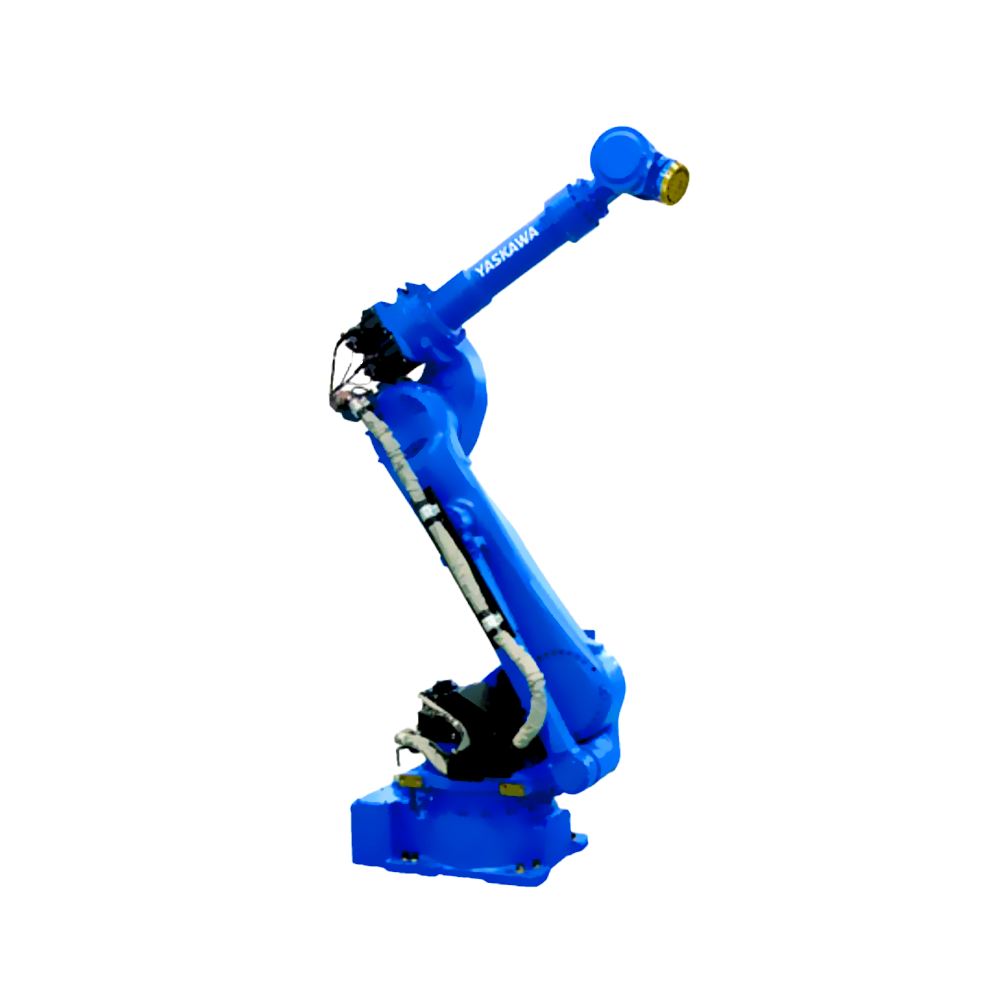
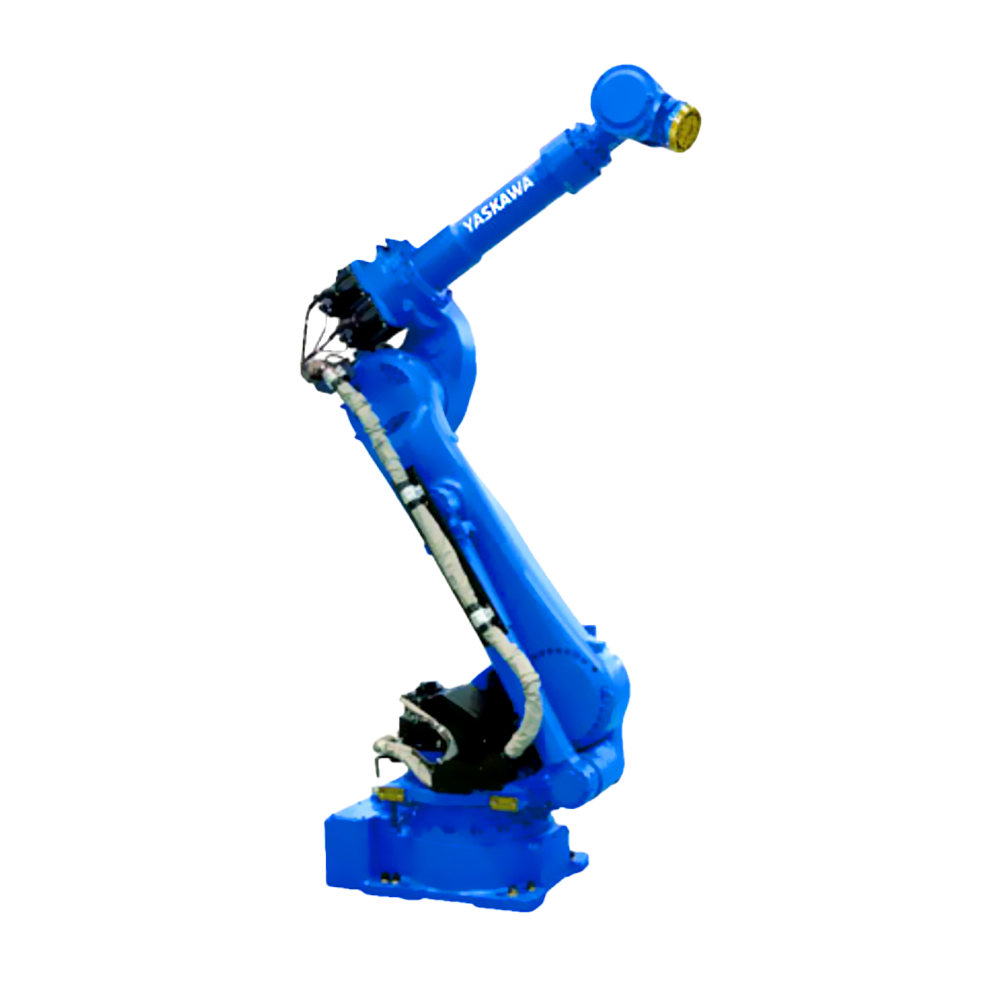
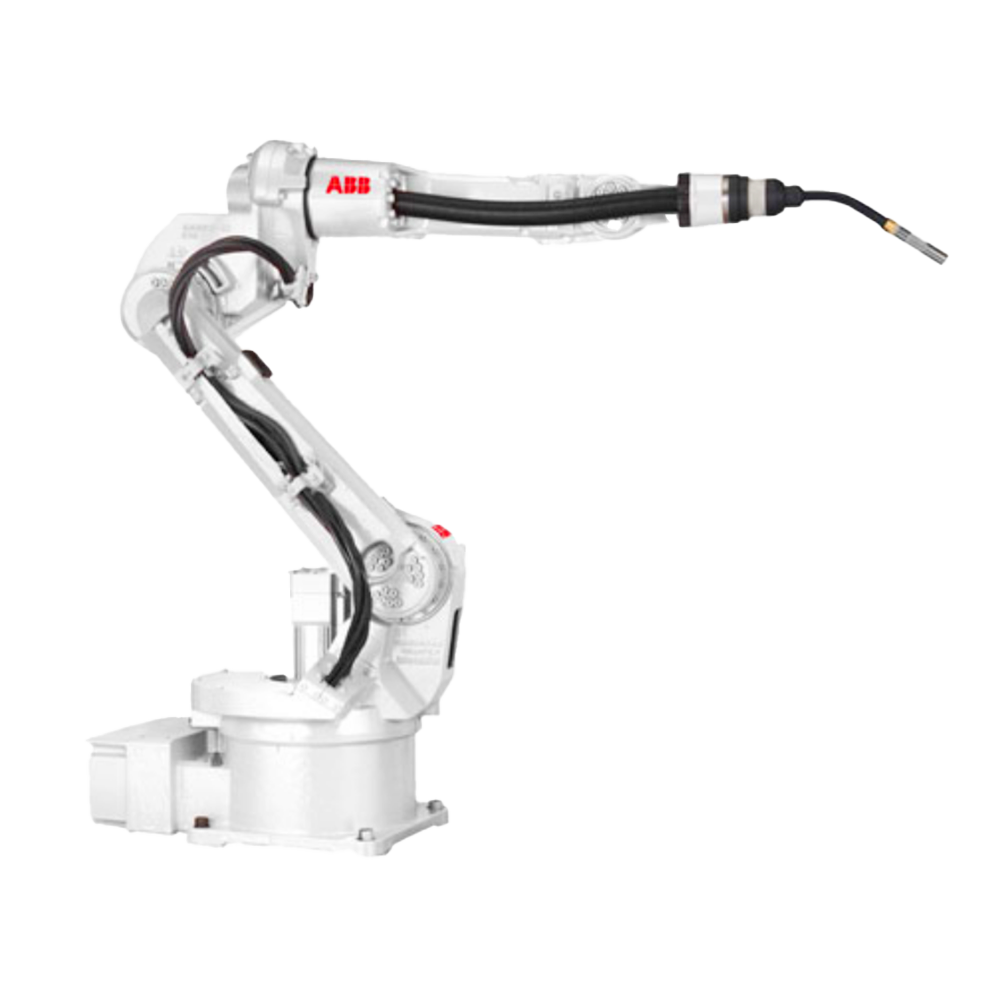
隨著電子技術(shù)、計(jì)算機(jī)技術(shù)、數(shù)控及機(jī)器人技術(shù)的發(fā)展,自動(dòng)焊接機(jī)器人, 從60年代開(kāi)始用于生產(chǎn)以來(lái),其技術(shù)已日益成熟。因此,在各行各業(yè)也得到了廣泛的應(yīng)用。
With the development of electronic technology, computer technology, numerical control, and robotics, automatic welding robots have become increasingly mature in technology since they were used in production in the 1960s. Therefore, it has also been widely applied in various industries.