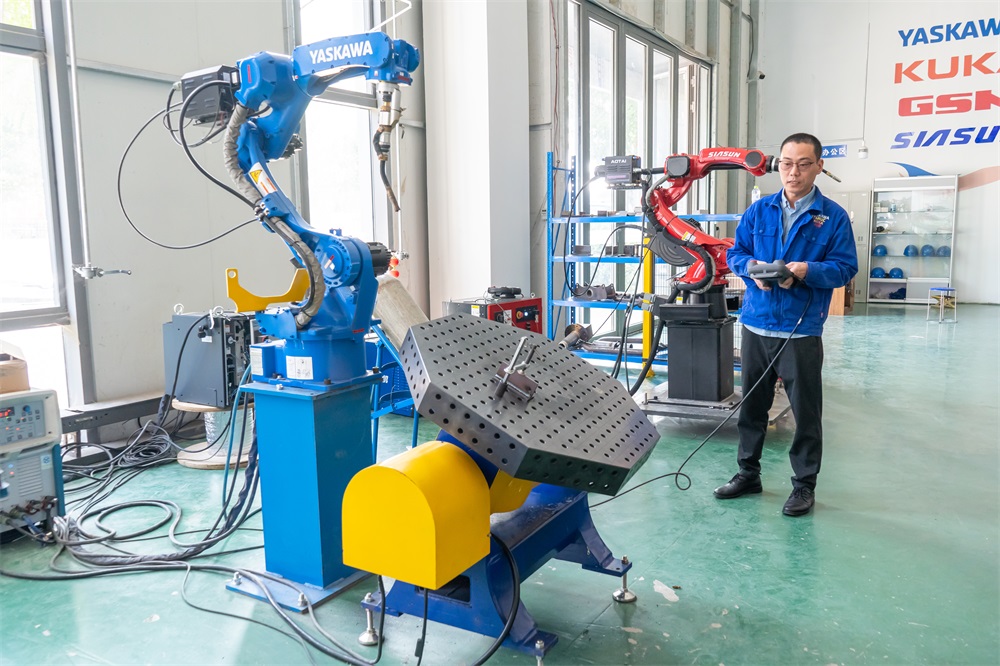
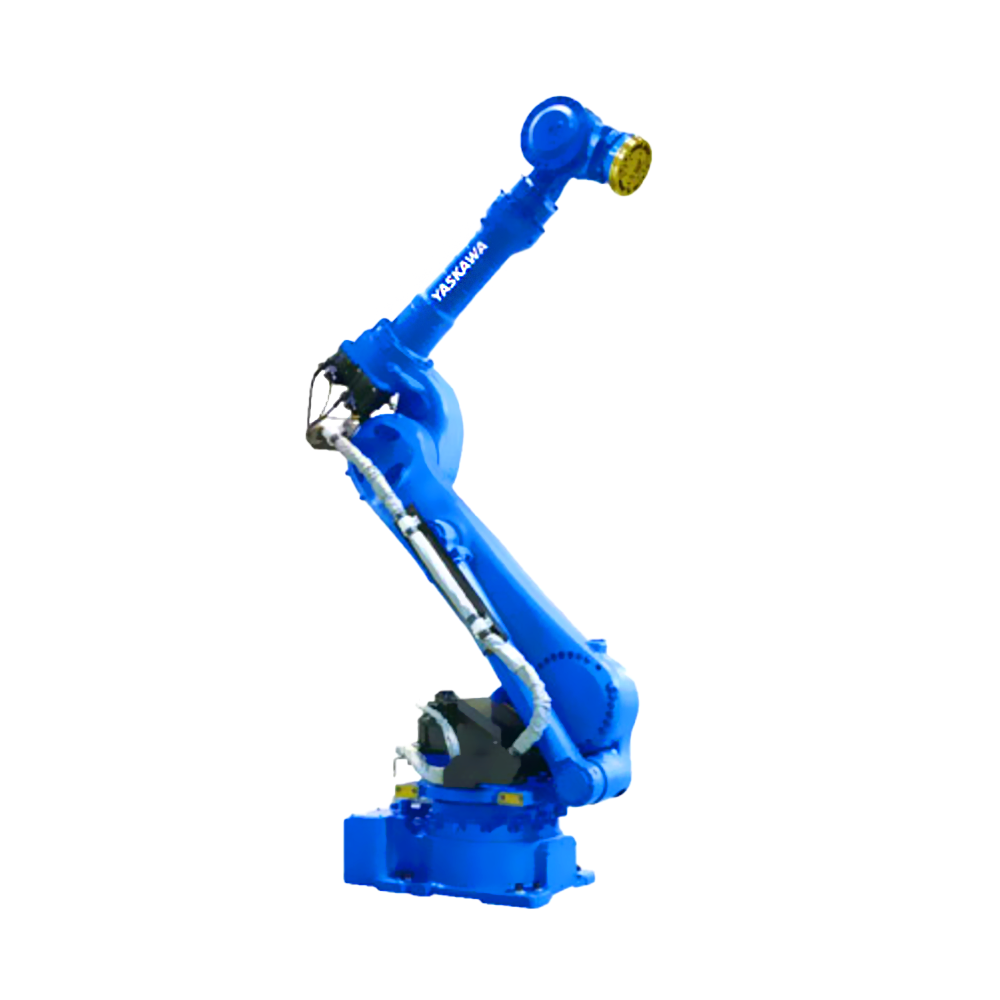
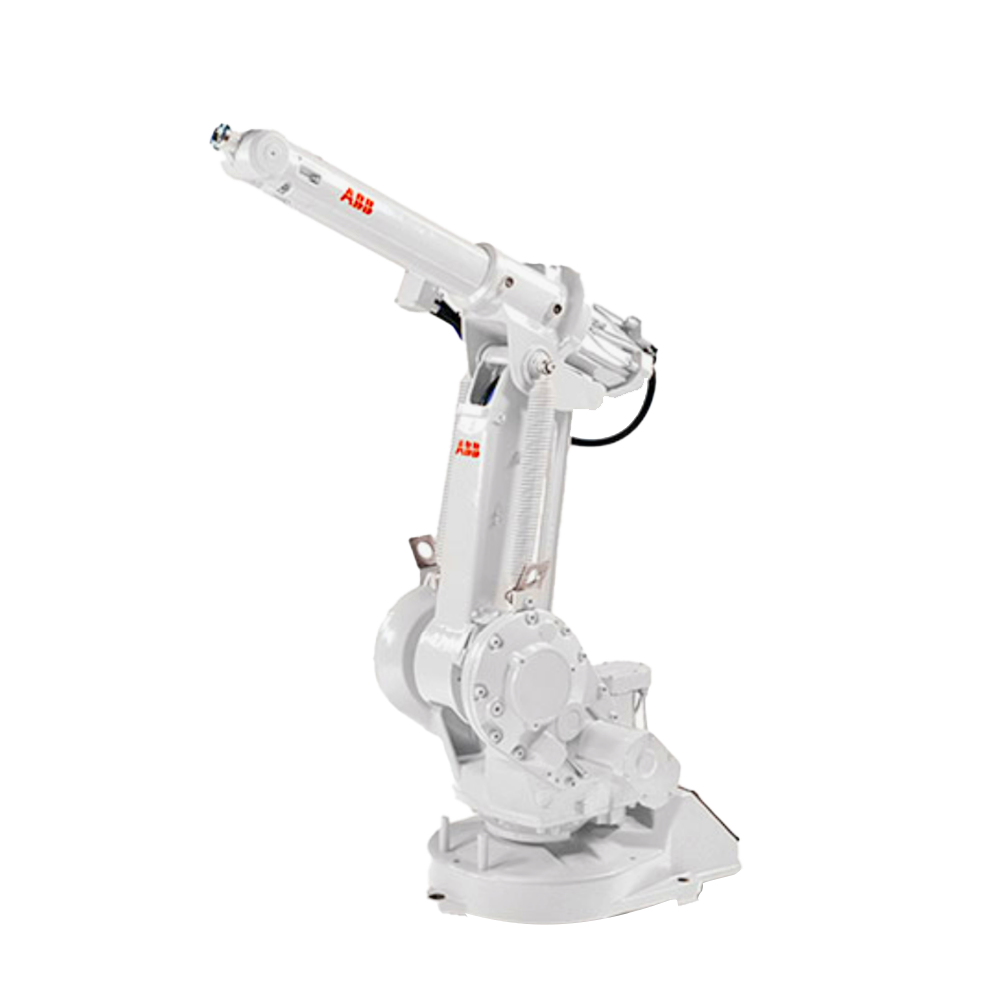
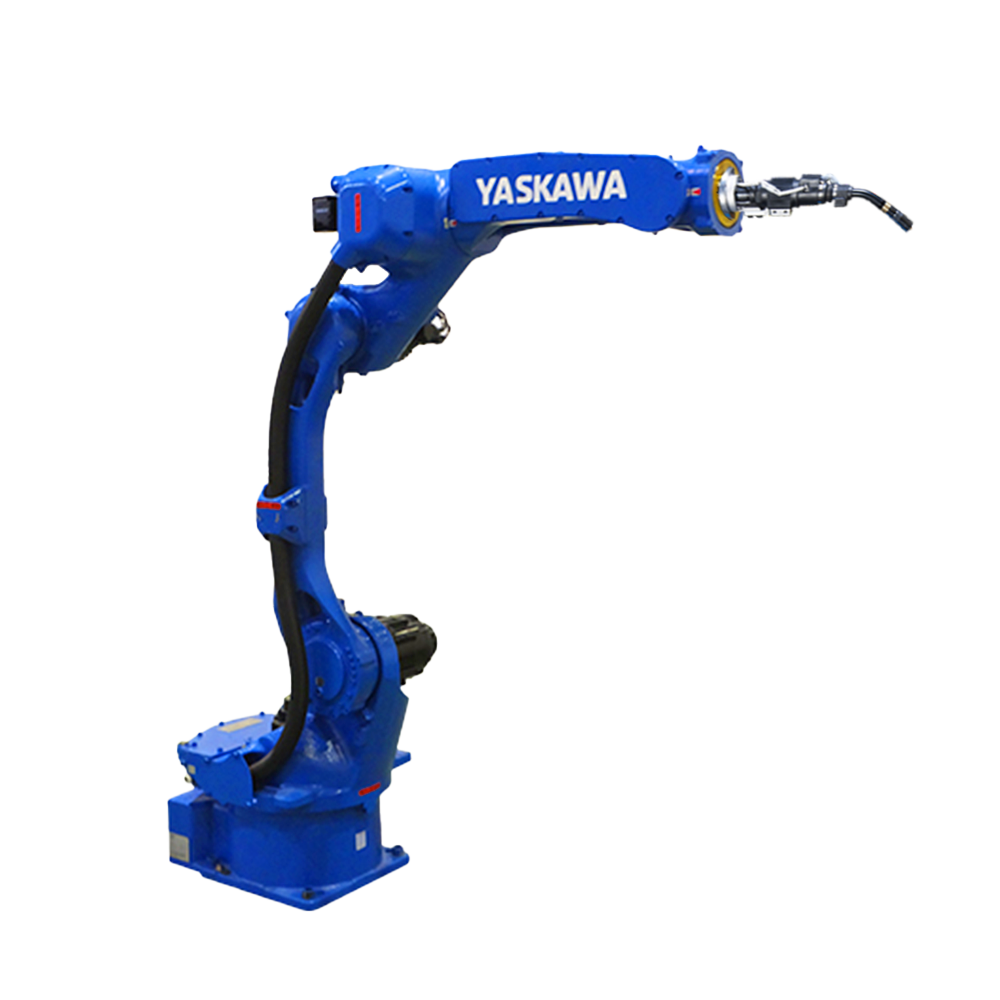
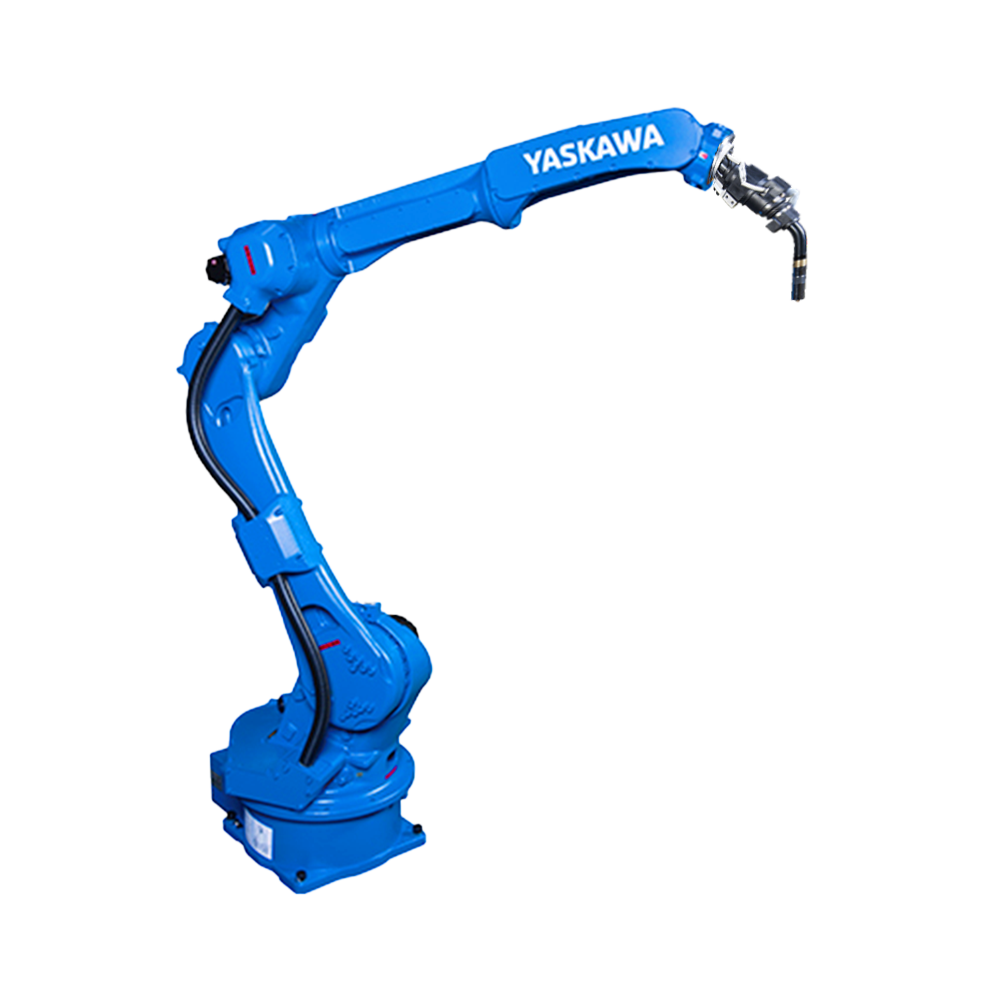
工業(yè)機(jī)器人主要由主體、驅(qū)動(dòng)系統(tǒng)和控制系統(tǒng)三個(gè)基本部分組成。
Industrial robots are mainly composed of three basic parts: the main body, driving system, and control system.
主體 - 即機(jī)座和執(zhí)行機(jī)構(gòu),包括臂部、腕部和手部,有的機(jī)器人還有行走機(jī)構(gòu)。大多數(shù)工業(yè)機(jī)器人有3-6個(gè)運(yùn)動(dòng)自由度,其中腕部通常有1-3個(gè)運(yùn)動(dòng)自由度。
The main body, namely the base and actuator, includes the arms, wrists, and hands, and some robots also have walking mechanisms. Most industrial robots have 3-6 degrees of freedom of motion, with the wrist typically having 1-3 degrees of freedom of motion.
驅(qū)動(dòng)系統(tǒng) - 包括動(dòng)力裝置和傳動(dòng)機(jī)構(gòu),核心為減速器以及伺服電機(jī),用以使執(zhí)行機(jī)構(gòu)產(chǎn)生相應(yīng)的動(dòng)作。
Drive system - including power device and transmission mechanism, with a reducer and servo motor as the core, to generate corresponding actions for the actuator.
控制系統(tǒng) - 是按照輸入的程序?qū)︱?qū)動(dòng)系統(tǒng)和執(zhí)行機(jī)構(gòu)發(fā)出指令信號(hào),并進(jìn)行控制。
Control system - It sends command signals to the driving system and executing mechanism according to the input program and controls them.
工業(yè)機(jī)器人分類
Classification of industrial robots
關(guān)于工業(yè)機(jī)器人的分類,國(guó)際上沒(méi)有指定統(tǒng)一的標(biāo)準(zhǔn),可按負(fù)載重量、控制方式、自由度、結(jié)構(gòu)、應(yīng)用領(lǐng)域等劃分。
There is no unified international standard for the classification of industrial robots, which can be divided by load weight, control method, degree of freedom, structure, application field, etc.
按照結(jié)構(gòu)形態(tài)分類如下。
Classified by structural form as follows.
按照應(yīng)用分類如下。
Classified by application as follows.
工業(yè)機(jī)器人產(chǎn)業(yè)鏈
Industrial robot industry chain
工業(yè)機(jī)器人產(chǎn)業(yè)鏈主要是由機(jī)器人零部件生產(chǎn)企業(yè)、機(jī)器人本體生產(chǎn)企業(yè)、代理商、系統(tǒng)集成商、終用戶構(gòu)成。本體是機(jī)器人產(chǎn)業(yè)鏈的核心,通常,本體企業(yè)設(shè)計(jì)本體、編寫軟件,采購(gòu)?fù)ㄟ^(guò)代理商銷售給系統(tǒng)集成商,系統(tǒng)集成商直接面向終端客戶。有的本體企業(yè)和代理商也會(huì)兼做系統(tǒng)集成商。
The industrial robot industry chain is mainly composed of robot component production enterprises, robot body production enterprises, agents, system integrators, and end users. Ontology is the core of the robotics industry chain. Typically, ontology enterprises design ontologies, write software, purchase and sell them to system integrators through agents, who directly target end customers. Some ontology enterprises and agents also work as system integrators.
從企業(yè)來(lái)看,ABB、發(fā)那科、庫(kù)卡和安川電機(jī)這四家企業(yè)是工業(yè)機(jī)器人的四大家族,成為世界主要的工業(yè)機(jī)器人供貨商,占據(jù)世界約 50% 的市場(chǎng)份額。
From the perspective of enterprises, ABB, Fanuc, Kuka, and Yaskawa Electric are the four major families of industrial robots, becoming the world's major suppliers of industrial robots and occupying about 50% of the world's market share.

工業(yè)機(jī)器人工作原理
Working Principles of Industrial Robots
機(jī)器人的工作原理是一個(gè)比較復(fù)雜的問(wèn)題。簡(jiǎn)單地說(shuō),機(jī)器人的原理就是模仿人的各種肢體動(dòng)作、思維方式和控制決策能力。從控制的角度,機(jī)器人可以通過(guò)如下四種方式來(lái)達(dá)到這一目標(biāo)。
The working principle of robots is a relatively complex problem. Simply put, the principle of robots is to mimic various human body movements, thinking patterns, and control decision-making abilities. From a control perspective, robots can achieve this goal in the following four ways.
“示教再現(xiàn)”方式:它通過(guò)“示教盒”或人“手把手”兩種方式教機(jī)械手如何動(dòng)作,控制器將示教過(guò)程記憶下來(lái),然后機(jī)器人就按照記憶周而復(fù)始地重復(fù)示教動(dòng)作,如噴涂機(jī)器人。
"Teaching and reproducing" method: It teaches the mechanical arm how to move through two methods: "teaching box" or "human hand handle". The controller remembers the teaching process, and then the robot repeats the teaching action in a cycle according to the memory, such as a spraying robot.
“可編程控制”方式:工作人員事先根據(jù)機(jī)器人的工作任務(wù)和運(yùn)動(dòng)軌跡編制控制程序,然后將控制程序輸入給機(jī)器人的控制器,起動(dòng)控制程序,機(jī)器人就按照程序所規(guī)定的動(dòng)作一步一步地去完成,如果任務(wù)變更,只要修改或重新編寫控制程序,非常靈活方便。大多數(shù)工業(yè)機(jī)器人都是按照前兩種方式工作的。
Programmable control method: The staff prepares a control program based on the robot's work task and motion trajectory in advance, and then inputs the control program to the robot's controller. Starting the control program, the robot completes the actions specified in the program step by step. If the task changes, it is very flexible and convenient to modify or rewrite the control program. Most industrial robots work in the first two ways.
“遙控”方式:由人用有線或無(wú)線遙控器控制機(jī)器人在人難以到達(dá)或危險(xiǎn)的場(chǎng)所完成某項(xiàng)任務(wù)。如防暴排險(xiǎn)機(jī)器人、軍用機(jī)器人、在有核輻射和化學(xué)污染環(huán)境工作的機(jī)器人等。
"Remote control" method: A person uses a wired or wireless remote control to control a robot to complete a task in a location that is difficult for people to reach or dangerous. Such as riot prevention and rescue robots, military robots, and robots working in environments with nuclear radiation and chemical pollution.
“自主控制”方式:是機(jī)器人控制中、復(fù)雜的控制方式,它要求機(jī)器人在復(fù)雜的非結(jié)構(gòu)化環(huán)境中具有識(shí)別環(huán)境和自主決策能力,也就是要具有人的某些智能行為。
Autonomous control method: It is the most advanced and complex control method in robot control, which requires robots to have the ability to recognize the environment and make autonomous decisions in complex and unstructured environments, that is, to have certain intelligent behaviors of humans.
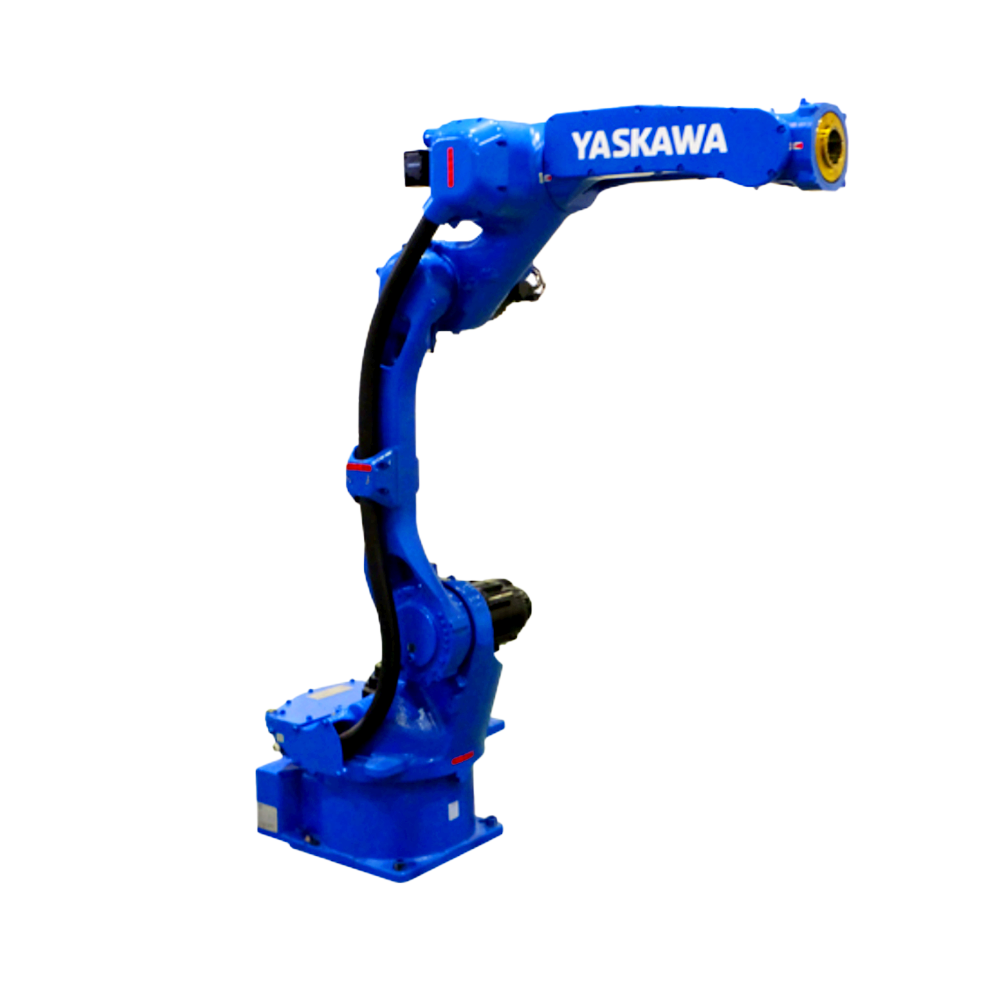
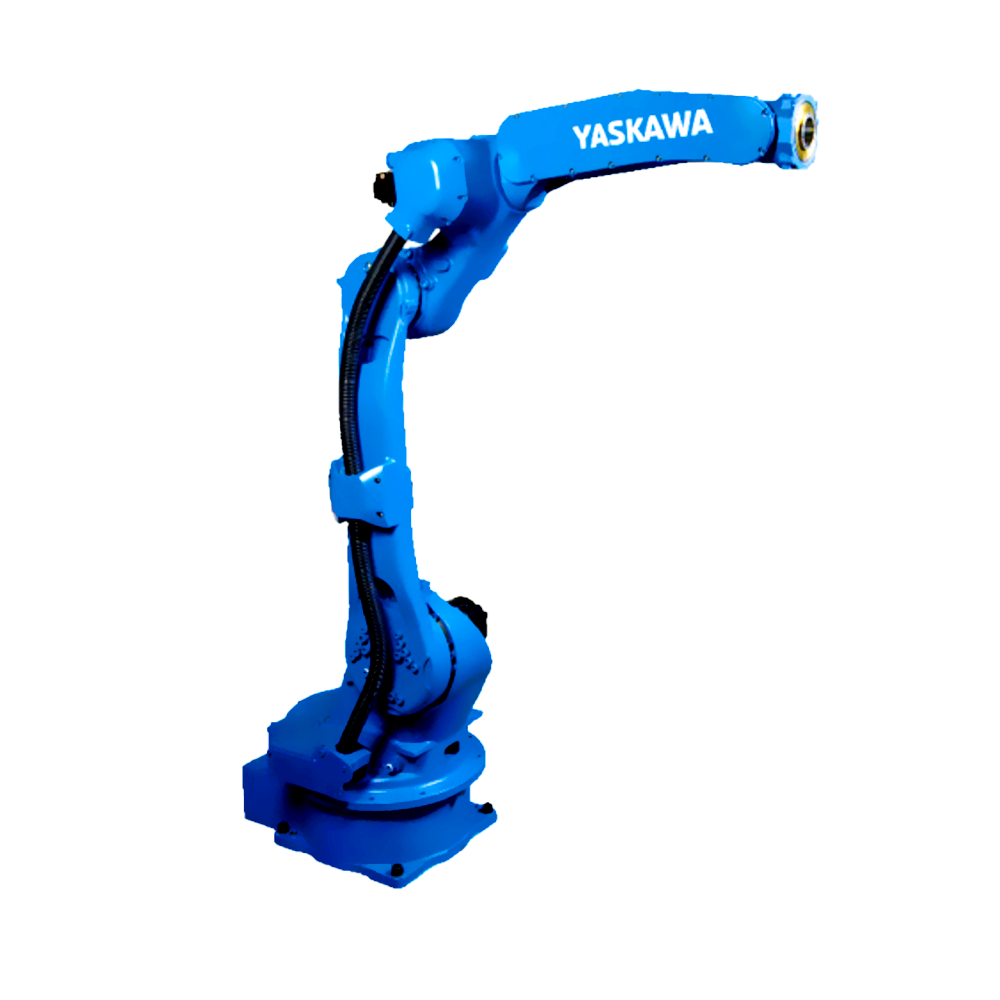
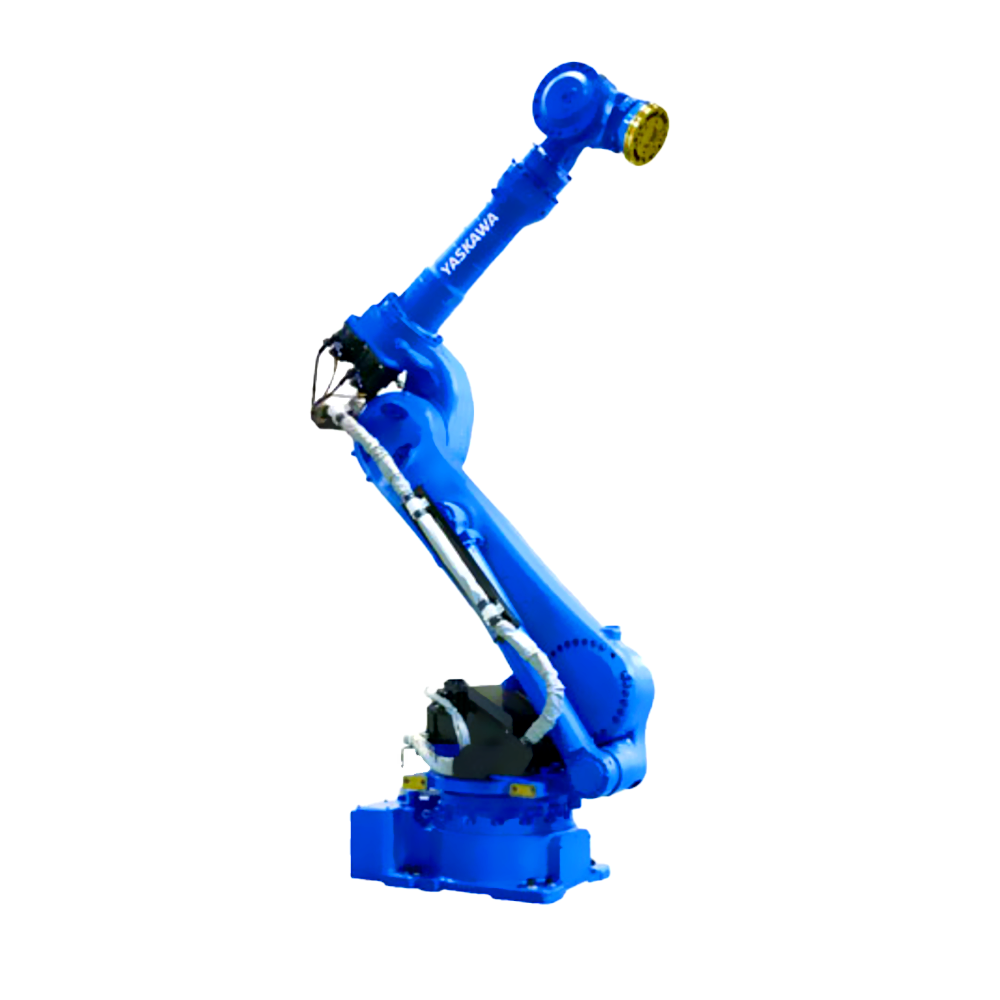
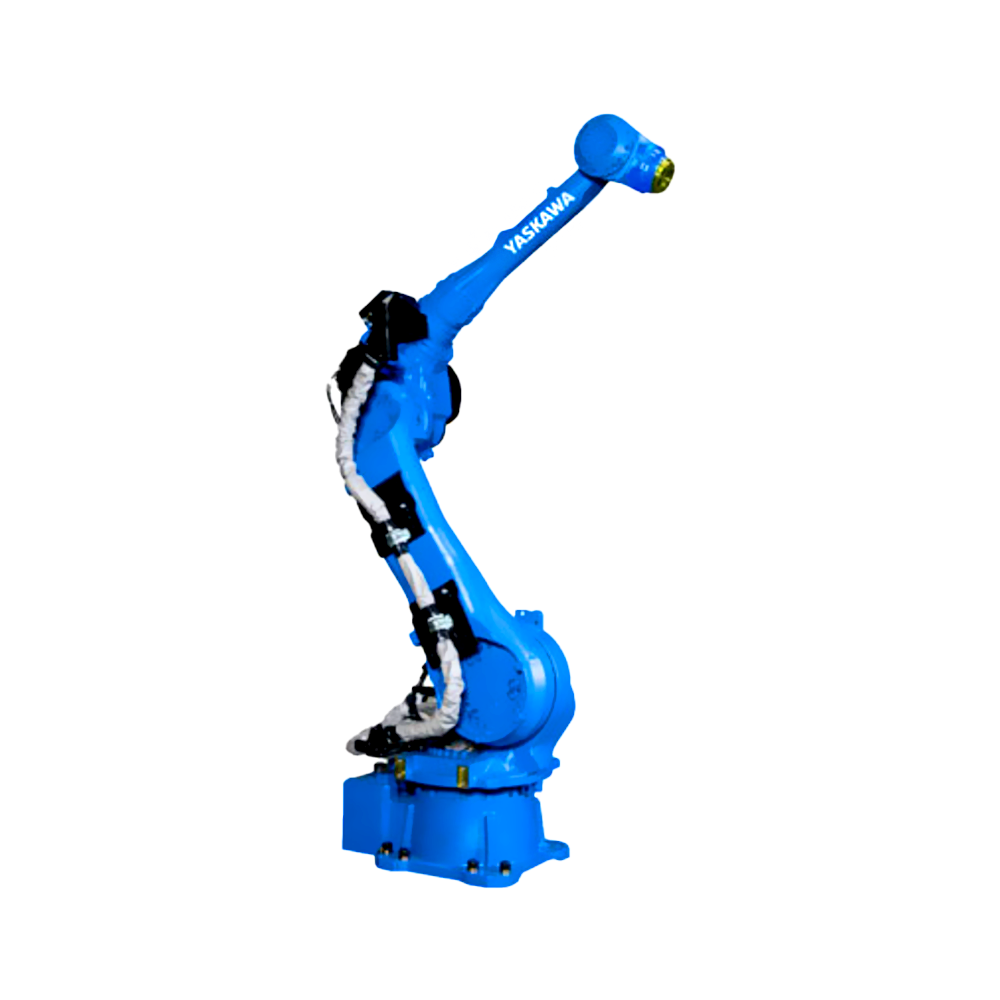
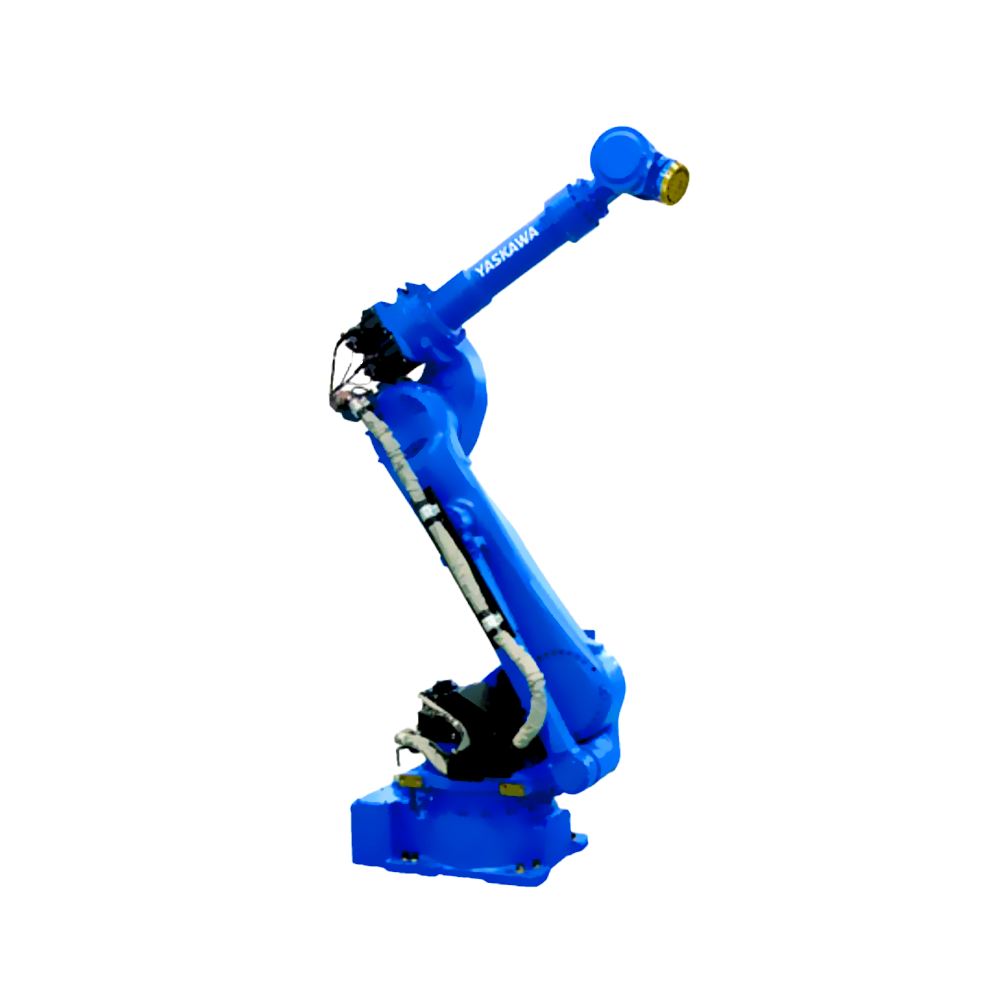
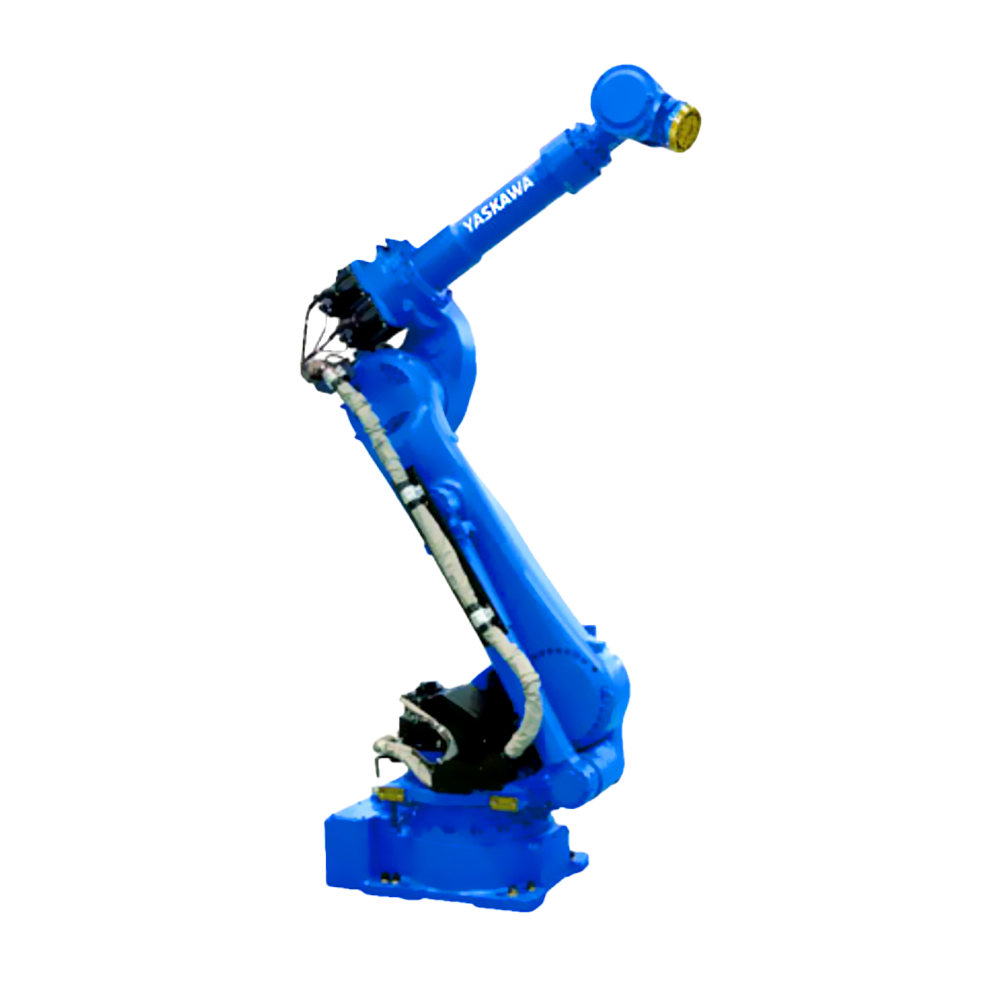
以六軸垂直多關(guān)節(jié)機(jī)器人為例(如下圖),通過(guò)機(jī)器人控制器及其控制系統(tǒng),可實(shí)現(xiàn)S軸回旋,L軸下臂傾動(dòng),U軸上臂傾動(dòng),R軸手臂橫擺,B軸手腕俯仰以及T軸的手腕回旋,實(shí)現(xiàn)六個(gè)軸的動(dòng)作操作與配合。
Taking a six axis vertical multi joint robot as an example (as shown in the figure below), the robot controller and its control system can achieve S-axis rotation, L-axis lower arm tilt, U-axis upper arm tilt, R-axis arm lateral swing, B-axis wrist pitch, and T-axis wrist rotation, achieving the operation and coordination of six axes.
以上的文章由山東軒燁機(jī)器人科技有限公司工業(yè)機(jī)器人提供分享,更多內(nèi)容請(qǐng)關(guān)注我們:http://www.2030588.com.
The above article is shared by Shandong Xuanye Robot Technology Co., Ltd. Industrial Robotics. For more content, please follow us: http://www.2030588.com.